Did you know that the current world population consumes 130,000 animals every minute? Add this to the fact that the world population is expected to reach 10 billion by 2050, and you are stuck with a hard question: Where will the food to feed all these people come from?
The World Resources Institute presents what it calls “a five-course menu of solutions.” For North America, one of the solutions is to cut the consumption of meat by half. Such advice is part of the reason the alternative meat market is growing exponentially.
Companies like Impossible Meats and Beyond Meat have successfully developed plant-based meat substitutes. But what is alternative meat? How is it made? Does it taste the same as real meat? Is it healthy?
If you are a grill master looking for answers to the above questions and many more, this article is for you.
- What Is Alternative Meat?
- How Does Alt Meat Taste?
- How Does Alt Meat Work On The Grill?
- Which Companies Are Behind Alt Meat?
- How Healthy Is Alt Meat Compared To Real Meat?
- How Does Lab-Grown Meat Compare To Alt Meat?
- How Is The Market Responding To Alt Meat?
- How Are Meat Producers And Food Chains Responding To Alt Meat?
- Why Is Alt Meat More Expensive Than Real Meat?
- What Is The Future Of Alt Meat?
What Is Alternative Meat?
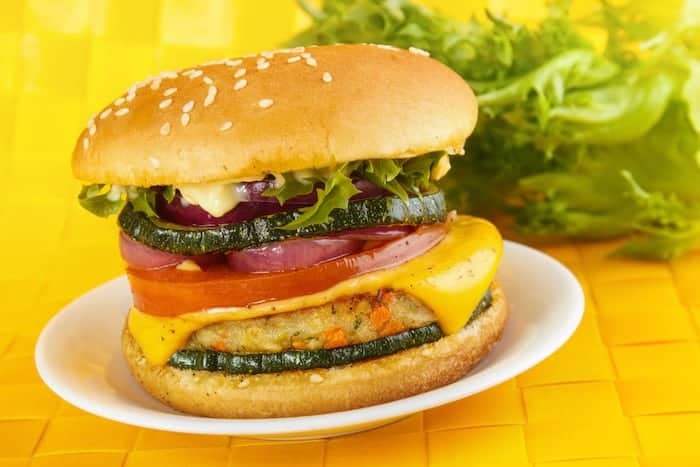

Alternative meat, also known as alt meat, fake meat, plant-based beef, chicken, or pork, is an imitation of meat. It is made from protein-based foods. The most common ingredients used to make alt meat include soy protein or pea protein. In producing alt meat, the aim is to create food that appears, cooks, and tastes like meat while also having the same amount of protein as real meat.
Alt meat is manufactured from several ingredients. Some common examples of these ingredients include a protein source, starch, extract from beet juice for color, oil, added vitamins, and salt.
How Does Alt Meat Taste?
It is one thing to make a product look and cook like real meat, but it’s another thing to get it to taste like actual meat. Writing for the news website Vox.com, Kelsey Piper says, “Everyone agrees that taste will be the big make-or-break factor for these companies [that manufacture alt meat].”
But what do those who have tried alt meat say?
In an article published by TheGuardian.com, Alyx Gorman quotes the advocacy group Choice, whose verdict was that “Supermarket vegan patties and minces fall short on flavor.”
The New York Times ran a blind tasting experiment involving three participants and alt meat products from six companies. While the general agreement among the testers seems to be that alt meat mostly tastes like real meat, some manufactures seem to do better than others. Writing about the experiment, Julia Moskin of The New York Times concludes that the alt meat products are not created equal.
A contributor on Quora posed the question, “Can’t we all eat ‘fake’ meat?” Adding, “It tastes just the same as ‘regular’ meat.” Someone answered, “I once ate a piece of fake ‘ham.’ I once fell face-first into a thorn bush. I can perfectly say that if I had a choice to repeat one of the two, it would be a very difficult choice.” Many other people answering the Quora question note that alt meat doesn’t taste like real meat.
The American chef and food writer, J. Kenji López-Alt, explains that the difference in taste can be attributed to the fact that “Beef fat … tends to melt slowly, over a wide temperature range.” Adding that “This slow release of fat results in juiciness that lingers as you chew.” On the other hand, he says the oil used in manufacturing alt meat “translates to bites that start off rich and juicy; but that juiciness wears off much quicker.”
How Does Alt Meat Work On The Grill?
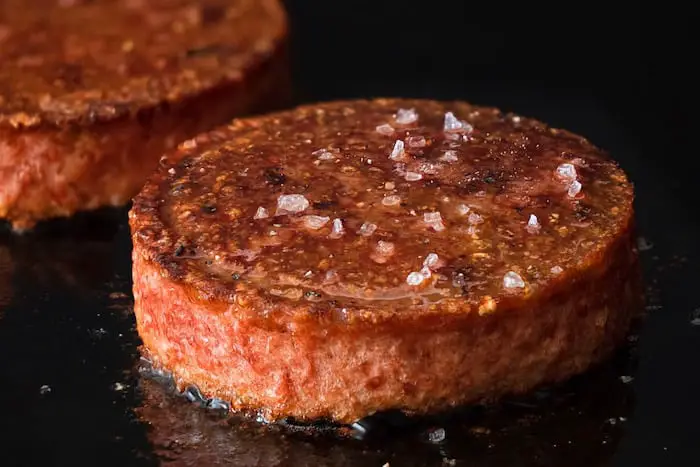

If alt meat is to be a genuine contender to replace real meat, it will need to perform like real meat on the grill. How has alt meat performed on the grill? Do you grill it in the same way as you do chicken or beef? A few people have shared their opinions on this subject.
López-Alt reviews alt meat from Beyond The Burger and says that it cooks like any other meat. He adds that “You can form it into patties of any shape and size, you can fry it, you can grill it, you can smash it, you could probably even cook it sous vide.” Sous vide is a French phrase that means cooking food in a vacuum, usually inside a plastic where the air has been removed.
However, López-Alt notes that alt meat “doesn’t brown in quite the same way that real beef does—the patties come out much crisper and crunchier on the exterior.”
If alt meat cooks in the same way as real meat on the grill, then you can cook it on a grill pan on your gas stove. Even though cooking on a gas stove may work better, you could also grill your alt meat using a grill pan on the electric burner.
Which Companies Are Behind Alt Meat?
If consumers have been showing a propensity to move toward alt meat, the business sector has not disappointed them. Several companies have come to the barbecue party with different types of alt meat. The leading firms in this area include Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, Redefine Meat, Taco Bell, and JUST.
How Healthy Is Alt Meat Compared To Real Meat?
To understand whether alt meat is healthier than real meat, we need to start by asking whether a plant-only diet is better than a diet that involves meat. However, things are not as simple as that. We also have to consider the processes used in manufacturing alt meat because excessive processing is generally considered to make food less healthy.
The American Heart Association cites some experts who note that even though many people believe that alt meat is healthy because it is plant-based, that view is not always accurate. This is especially the case if you consider the amount of processing involved in manufacturing alt meat.
The American Heart Association quotes a professor of food science and human nutrition at the University of Maine, Mary Ellen Camire, who says, “Iron from beef is very well absorbed, but plant iron not so much so.” Adding, “The big thing is vitamin B12 because you can only get that from animal products or supplements. So for some people, that is a risk factor. They may be at risk for developing anemia.”
An article published by the Oklahoma-based health care system, INTEGRIS Health, reports that many of the ingredients used in making alt meat “include chemical compounds such as methylcellulose, soy leghemoglobin, and zinc gluconate.” The same source adds that the burgers have the same number of calories compared to real meat, if not higher. The same can be said about the amount of fat.
The short answer to the question of whether alt meat is healthier than real meat is that it is not. But this doesn’t mean that real meat is healthier than alt meat either. INTEGRIS Health suggests that the secret to healthy eating is “a diet that encourages whole, plant-based foods with limited meat, dairy, processed foods, and eggs.”
How Does Lab-Grown Meat Compare To Alt Meat?
Researchers are currently working on another type of alternative meat: lab-grown meat (Also known as culture- or cell-based meat). The difference between alt meat and lab-grown meat is that while the former attempts to imitate meat using plant-based ingredients, the latter makes the meat from actual animal cells. Thus, lab-grown meat can be viewed as real meat grown in the lab.
At this point, it’s a challenge to compare alt meat and lab-grown meat because the latter is still in the early stages of development. For example, ScientificAmerican.com reports that “In 2013 when a burger made from lab-grown meat was presented to journalists, the patty cost more than $300,000 to produce and was overly dry (from too little fat).” The cost has since come down to about $600 per burger.
How Is The Market Responding To Alt Meat?
The availability of information and growing consciousness among consumers result in people who are more careful about what they eat and how their eating habits affect the environment.
The Plant Based Food Association reports that the U.S. alternative food sector grew 27% in 2020. The same source also reports that in the same year, “57 percent of all U.S. households purchased plant-based foods (that’s over 71 million households) – up from 53 percent in 2019.”
How Are Meat Producers And Food Chains Responding To Alt Meat?

As expected, producers of real meat are worried about the disruptive effects of alt meat on their business models. They have responded by launching lawsuits to try and prevent the alt meat industry from using the word meat in describing their products.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) says that “The rapid rise of the plant-based market has producers, retailers and food brands playing catch-up.” Adding, “New entrants like Beyond Meat, Just, and Impossible Foods have forced established players to innovate, invest and launch new products to avoid a disruption of their existing brands.”
Probably sensing that it’s inevitable that alt meat will continue to eat into the real meat market share, the WEF says that the real meat market is adopting an “If you can’t beat them, join them” attitude. It is doing this through introducing alt meat products of their own or acquiring startups in the alt meat space.
Why Is Alt Meat More Expensive Than Real Meat?
While we are no longer in 2013 when producing the patty for an alt meat burger cost more than $300,000, alt meat is still more expensive than regular meat. But why is this the case? Liz Specht, VP of Science & Technology at The Good Food Institute, provides the answer in an article published by her organization.
Specht says that the main reason alt meat is more expensive at the moment is simply that demand outstrips supply. Companies in the alt meet space are therefore taking advantage of the market conditions and making as much profit as possible. Also, these companies need more money to scale.
Other reasons advanced by Specht include underdeveloped ingredient supply chains, infrastructure, and high research and development costs. However, it is expected that as more companies enter the alt meat market and more products appear on shelves, the prices will start coming down.
What Is The Future Of Alt Meat?
Companies in the alt meat space are attracting the attention of funders and consumers. Jordan Bar Am, Partner at McKinsey & Company, predicts the future: “My craziest prediction about protein consumption in 2030 is that in every fast-food and fast-casual outlet and fine-dining establishment, there will be multiple options on the menu for flexitarian and ‘lessitarian’ consumers.”
The Plant Based Foods Association believes that the growth in plant-based meat alternatives is sustainable. What is this view based on? Seventy-seven percent of shoppers surveyed by Cypress Research Group indicated that they had purchased a plant-based product in the last six months, and 90 percent of these indicated that the change toward plant-based products would be permanent.




